The terms cardiac arrest and heart attack are often used interchangeably, but they’re actually two very different medical conditions. While a cardiac arrest refers to the heart malfunctioning, a heart attack is a circulation problem. To help distinguish between the two conditions, we’re explaining the difference between a cardiac arrest and a heart attack.
What is a cardiac arrest?
A cardiac arrest is when the heart suddenly stops beating, usually due to an issue with the electrical signals in your heart. When your heart stops beating, it will no longer be pumping blood around your body. This will lead to your brain being starved of oxygen, and if untreated it will be fatal.
The signs:
There are often no symptoms prior to a cardiac arrest. If someone collapses suddenly and is in cardiac arrest they will be:
- Unconscious
- Unresponsive
- Not breathing or not breathing normally
The treatment:
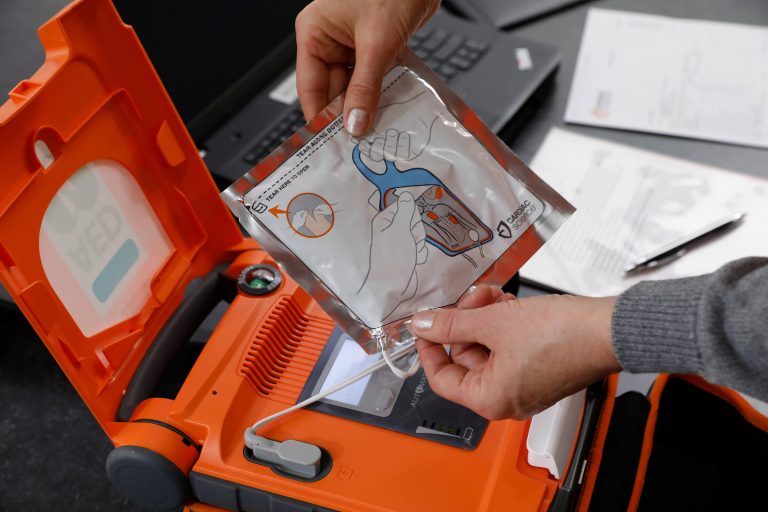
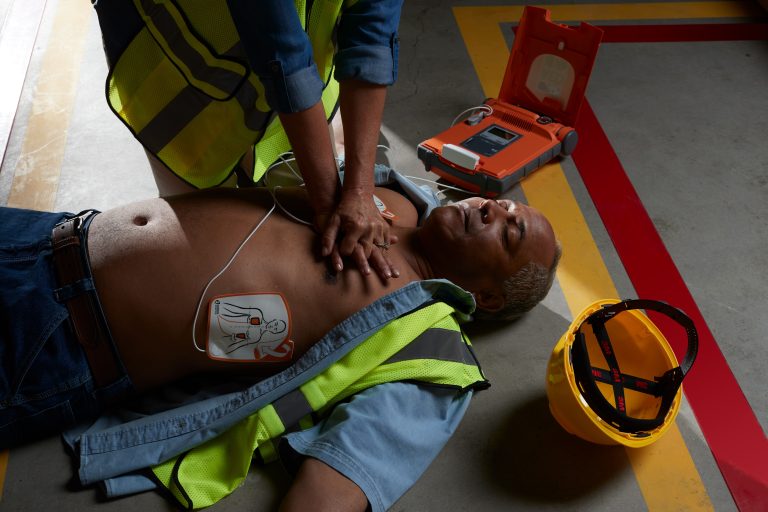
If you think someone is in cardiac arrest, call 999 immediately and start giving high quality CPR. If there is someone else with you, send them to find a defibrillator. The patient could have a 70% chance of survival if defibrillation happens within three minutes of a cardiac arrest. However, with every minute that passes, their chance of survival will decrease by 10%.
Not sure how a defibrillator works? Find out more by reading our guide on how to use a defibrillator.
Want to know how to give CPR? Read our blog about how to give high quality CPR.
What is a heart attack?
A heart attack, otherwise known as a myocardial infarction, is when the supply of blood to the heart suddenly stops, usually caused by clot blocking the blood flow. A sustained lack of blood flow to the heart can seriously damage the organ and can be fatal.
The signs:
There are a number of symptoms which an individual may experience if they’re suffering from a heart attack. These include:
- Chest pain (this can feel like the chest is being squeezed or pressed by a heavy object, and can radiate to other areas of the body)
- Shortness of breath
- Feeling weak or lightheaded
- Feeling very anxious
The treatment:
It is usually a combination of the above symptoms which indicate a heart attack.
Cardiac arrest vs heart attack
If you think someone is suffering from a heart attack, call 999 immediately.
Despite a cardiac arrest and a heart attack being two different conditions, there is a link between them. Sudden cardiac arrest can occur after a heart attack or even during the recovery. Although most heart attacks don’t lead to a cardiac arrest, they do increase a person’s risk of having one.
Both a cardiac arrest and a heart attack are medical emergencies and immediate action needs to be taken if you see the signs of either. If you’d like to increase the chances of your colleagues or pupils surviving a cardiac arrest, get in touch today to discuss getting a defibrillator for your school or workplace.